Demystifying Earned Value Management (EVM) for PMP Exam Success
Earned Value Management (EVM) is a powerful tool that integrates cost, scope, and schedule to accurately measure project performance. For those preparing for the Project Management Professional (PMP) exam, a solid understanding of EVM is crucial, particularly within the “Project Cost Management” Knowledge Area. In this article, we’ll break down the core principles of EVM and provide valuable insights to help you approach EVM-related questions effectively in the PMP exam.
Understanding the Components of EVM
EVM revolves around three primary components, each representing a different facet of project costs:
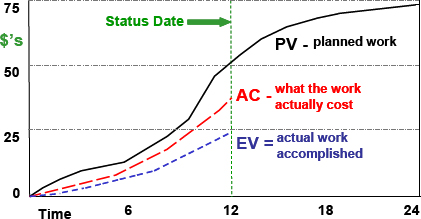
- Budget for Costs: Budget Cost of Work Scheduled (BCWS) or Planned Value (PV)
- Description: BCWS or PV represents the planned cost allocated for resources and activities up to the current status date.
- Example: Imagine planning a project to install a new software system, and you’ve allocated $10,000 for development up to a certain date. This $10,000 is your Planned Value (PV).
- Amount of Work Valued Done: Budgeted Cost of Work Performed (BCWP) or Earned Value (EV)
- Description: EV is derived from the value of work completed based on the budget, providing a measure of work accomplished.
- Example: Let’s say your software development team has completed work worth $7,000 according to the planned budget. This $7,000 is your Earned Value (EV).
- Actual Costs Applied: Actual Cost of Work Performed (ACWP) or Actual Costs (AC)
- Description: AC represents the actual expenditure on the work that has been completed.
- Example: After reviewing the financial records, you find that your team has actually spent $6,000 for the completed work. This $6,000 is your Actual Cost (AC).
Essential EVM Formulas for PMP Exam
Understanding the EVM formulas is crucial for success in the PMP exam. Here are the key formulas and their meanings:
- Cost Variance (CV)
- Formula: CV = EV – AC
- Description: Indicates cost performance in relation to the work done.
- Example: CV = $7,000 (EV) – $6,000 (AC) = $1,000 (Cost Variance)
- Schedule Variance (SV)
- Formula: SV = EV – PV
- Description: Measures schedule performance in relation to the budget.
- Example: SV = $7,000 (EV) – $10,000 (PV) = -$3,000 (Schedule Variance)
- Cost Performance Index (CPI)
- Formula: CPI = EV / AC
- Description: Indicates work performance per dollar spent.
- Example: CPI = $7,000 (EV) / $6,000 (AC) = 1.17 (Cost Performance Index)
- Schedule Performance Index (SPI)
- Formula: SPI = EV / PV
- Description: Measures work speed in relation to the planned schedule.
- Example: SPI = $7,000 (EV) / $10,000 (PV) = 0.7 (Schedule Performance Index)
- To-Complete Performance Index (TCPI)
- Formula: TCPI = (BAC – EV) / (Target – AC)
- Description: Predicts future efficiency needed to reach a target.
- Example: If the target cost is $15,000 and AC is $6,000, TCPI = ($15,000 – $7,000) / ($15,000 – $6,000) = 1.29 (To-Complete Performance Index)
- Estimate To Complete (ETC)
- Formulas: ETC = BAC – EV or ETC = (BAC – EV)/ CPI
- Description: Estimates remaining costs in a straightforward manner.
- Example: ETC = $20,000 (BAC) – $7,000 (EV) = $13,000 (Estimate To Complete)
- Estimate At Complete (EAC)
- Formulas: EAC = AC + (BAC – EV) or EAC = AC + (BAC – EV) / CPI
- Description: Estimates the final project cost based on performance.
- Example: EAC = $6,000 (AC) + ($20,000 (BAC) – $7,000 (EV)) = $19,000 (Estimate At Complete)
- Variance at Completion (VAC)
- Formula: VAC = BAC – EAC
- Description: Indicates budget overruns or savings at the project’s end.
- Example: VAC = $20,000 (BAC) – $19,000 (EAC) = $1,000 (Variance at Completion)
Mastering EVM for PMP Exam Success
In real-world scenarios, ETC and EAC calculations may vary. However, for the PMP exam, always analyze the question’s context to guide your approach. For ETC, evaluate whether costs align with the budget or past efficiency. EAC is simply AC plus the projected remaining costs (ETC). VAC provides insights into budget overruns or savings by comparing BAC to EAC.
In conclusion, mastering EVM and its formulas is paramount for PMP exam success, particularly within the context of “Project Cost Management.” A thorough understanding of EVM will not only help you excel in the exam but also enhance your project management skills for future projects.
Best of luck on your journey to PMP certification success!
Summary Table
| Symbol | Name | Formula | Description | Interpretation of Result |
| Inputs | ||||
| PV | Planned Value | The value of the portion of the task that is supposed to have been completed | ||
| EV | Earned Value | The value of the portion of the task that is actually completed | ||
| AC | Actual Cost | The actual cost of the task to date | ||
| BAC | Budget at Completion | Total overall project budget (planned) | ||
| Outputs – Current Status | ||||
| SV | Schedule Variance | SV = EV – PV | The amount that the task is ahead or behind schedule, expressed as a task value |
SV < 0 = behind schedule SV > 0 = ahead of schedule |
| SPI | Schedule Performance Index | SPI = EV/PV | The amount that the task is ahead or behind schedule, expressed as a percentage of the task |
SPI < 1 = behind schedule SPI > 1 = ahead of schedule |
| CV | Cost Variance | CV = EV – AC | The amount that the task is over or under budget, expressed as a task value |
CV < 0 = over budget CV > 0 = under budget |
| CPI | Cost Performance Index | CPI = EV/AC | The amount that the task is ahead or behind schedule, expressed as a percentage of the task |
CPI < 1 = over budget CPI > 1 = under budget |
| Outputs – Forecast | ||||
| EAC | Estimate at Completion | EAC = BAC/CPIEAC = AC + (BAC – EV)EAC = AC + [(BAC – EV)/(SPI x CPI)]EAC = AC + ETC | The estimated project budget at the end of the project, given current project budget status | |
| ETC | Estimate to Complete | ETC = EAC – ACETC = new estimate | The expected cost to finish the project | |
| VAC | Variance at Completion | VAC = BAC – EAC | The expected cost variance at the end of the project, given current project status |
VAC < 0 = over budget VAC > 0 = under budget |
| TCPI | To Complete Performance Index | TCPI = (BAC – EV) / (BAC – AC)TCPI = (BAC – EV) / (EAC – AC) | The CPI required to complete the project on budget |
TCPI < 1 = under budget TCPI > 1 = over budget |
Tags: #EarnedValueManagement #EVM #ProjectManagement #PMPExam #PMPCertification #ProjectCostManagement #ProjectPerformance #CostVariance #ScheduleVariance #CostPerformanceIndex #SchedulePerformanceIndex #ToCompletePerformanceIndex #EstimateToComplete #EstimateAtComplete #VarianceAtCompletion #ProjectPlanning #BudgetManagement #WorkPerformance #ProjectMetrics #PMPPreparation
Learn more about Gantt Charts: Definition, Benefits, and How They’re Used here: Gantt Chart
Tag:#BudgetManagement, #CostPerformanceIndex, #CostVariance, #EarnedValueManagement, #EstimateAtComplete, #EstimateToComplete, #EVM, #PMPExam, #PMPPreparation, #ProjectManagement, #ProjectMetrics, #ProjectPerformance, #ProjectPlanning, #SchedulePerformanceIndex, #ScheduleVariance, #ToCompletePerformanceIndex, #VarianceAtCompletion, #WorkPerformance